N-Acetyl Cysteine, commonly known as NAC, is a derivative of the amino acid L-cysteine and is lauded for its antioxidant properties. In the world of bodybuilding, supplements are meticulously scrutinized for their ability to enhance muscle growth and recovery. NAC, standing out among numerous options, is linked to a variety of health benefits that may support athletic performance. It serves as a precursor to glutathione, a potent antioxidant that plays a critical role in reducing oxidative stress and aiding in recovery from intense physical activity.
The supplementation of NAC in sports and bodybuilding circles draws attention due to its potential impact on performance and health. Bodybuilders often face physical stress from their rigorous training regimens, and the inclusion of supplements such as NAC is investigated to understand how it can contribute to the reduction of inflammation and improve recovery times. That said, its use is not without a need for caution and understanding of appropriate dosage, as the safety profile and potential side effects are of equal importance to those considering this supplement.
Quick Summary
- NAC is a supplement used for its antioxidant effects, potentially enhancing recovery in bodybuilding.
- It contributes to muscle health by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, which may improve athletic performance.
- Safe supplementation requires knowledge of dosage guidelines and potential side effects.
NAC and Its Role in the Body
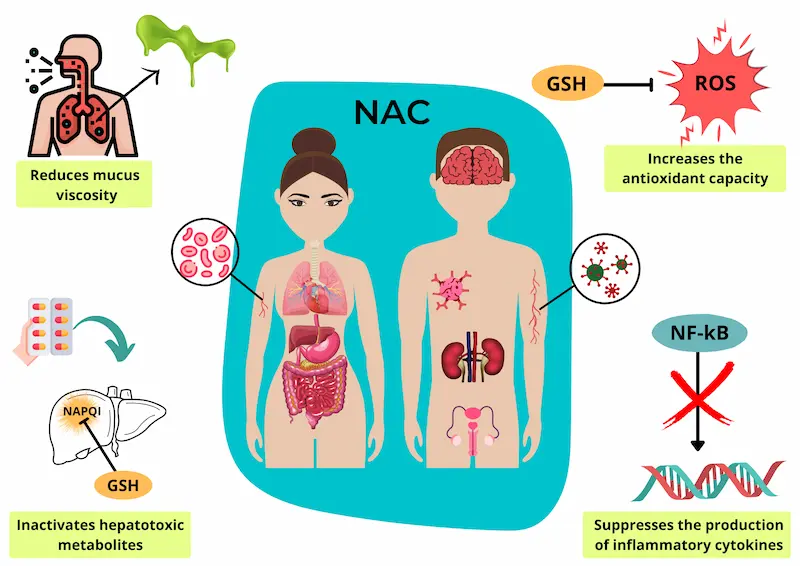
N-Acetyl Cysteine (NAC) is integral in bodybuilding for its support in reducing oxidative stress and aiding in recovery. It plays a crucial role in synthesizing glutathione, a significant antioxidant in the body. This section explores the composition and properties of NAC, its involvement in glutathione production, and its antioxidant and detoxifying functions.
Chemical Composition and Properties
NAC is a modified form of the amino acid cysteine, with an acetyl group attached that enhances its stability and bioavailability. Chemically, NAC is known as N-acetyl-L-cysteine and possesses a thiol side chain which is reactive and capable of interacting with free radicals and toxins.
Molecular Formula: C5H9NO3S
Molar Mass: 163.19 g/mol
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Solubility | Water, Alcohol |
| Melting Point | 109-110°C |
| Stability | Stable under normal conditions |
Biosynthesis of Glutathione
The body’s biosynthesis of glutathione, a tripeptide comprised of glutamine, glycine, and cysteine, is critically dependent on the availability of cysteine. NAC donates its cysteine to help form glutathione, boosting the body’s natural stores. Glutathione is present in almost all cells and plays a key role in neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS) and maintaining redox balance.
| Amino Acid | Role in Glutathione |
|---|---|
| Glutamine | Precursor |
| Glycine | Precursor |
| Cysteine | Rate limiting factor |
Antioxidant and Detoxifying Functions
NAC exhibits robust antioxidant properties by directly scavenging free radicals and replenishing intracellular levels of glutathione. It helps mitigate oxidative stress in cells, which is particularly prevalent during intense physical exercise such as bodybuilding. This reduction in oxidative damage is believed to aid in muscle recovery and may reduce muscle fatigue. Additionally, NAC serves as a detoxifying agent by binding to various toxins, facilitating their removal from the body.
| Function | Effect |
|---|---|
| Scavenging | Directly neutralizes ROS |
| Replenishing | Increases glutathione levels |
| Detoxifying | Binds to toxins for excretion |
Health Benefits of NAC Supplementation
N-Acetyl Cysteine (NAC) is known for its array of health benefits, particularly in bodybuilding where it supports various bodily functions. This section delves into how NAC supplementation can be beneficial.
Combating Oxidative Stress and Free Radicals
NAC serves as a precursor to glutathione, one of the body’s most potent antioxidants. It helps to neutralize harmful free radicals, which are generated during intense exercise, reducing oxidative damage to muscle tissues.
Support for Liver Health
The liver is pivotal in metabolizing nutrients and detoxifying the body. NAC’s role as an anti-inflammatory and antioxidant agent aids in protecting the liver from damage and supports its detoxification pathways.
Immune System Enhancement
NAC supplementation can bolster the immune system. Its ability to boost glutathione levels not only provides antioxidant benefits but also enhances the immune response, crucial for athletes undergoing heavy training cycles.
Respiratory Health Improvement
Intense exercise can sometimes compromise respiratory health. NAC has been observed to improve respiratory function by thinning mucus and reducing inflammation, facilitating better breathing and oxygen delivery to muscles.
Influence on Mental Health Conditions
Mental health is a critical component of overall wellbeing. Research suggests NAC might help in the management of certain mental health conditions such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and OCD by modulating neurotransmitters and reducing oxidative stress in the brain.
NAC in Sports and Bodybuilding
N-Acetyl Cysteine (NAC) is a supplement derived from the amino acid L-cysteine, touted for its role in muscle recovery and its potential impact on athletic performance through enhancing detoxification and immune function.
Muscle Recovery and Endurance
NAC plays a vital role in the synthesis of glutathione, an antioxidant that helps in reducing muscle damage and inflammation post-exercise. Studies suggest that athletes using NAC may experience less muscle soreness and improved recovery times. This can be crucial for endurance athletes who engage in prolonged physical exertion.
- Glutathione synthesis: Essential for reducing oxidative stress in muscles during and after workouts.
- Inflammation: May help alleviate post-workout inflammation, which is often a byproduct of intense physical activities.
Oxygen Utilization and Athletic Performance
NAC may enhance athletic performance by optimizing oxygen utilization in tissues. This is crucial for endurance sports where efficient oxygen consumption can prolong performance.
- Efficient breathing: NAC is known for its mucolytic effect, which helps in breaking down mucus in the respiratory tract, potentially improving breathing during exercise.
- Oxygen efficiency: Better oxygenation of muscle tissue can enhance endurance during prolonged sports activities.
Safety and Dosage Considerations for Athletes
While NAC can be beneficial, it is important that athletes adhere to safe dosage guidelines to avoid adverse effects.
- Recommended dosage: Athletes are often advised to take 600-1800 mg of NAC per day, split into multiple doses.
- Side effects: Possible side effects at high doses include gastrointestinal discomfort, rash, and headache.
Safety Profile and Potential Side Effects
N-acetylcysteine (NAC) is commonly used by bodybuilders to support liver health and detoxification. However, it’s important to understand its safety profile and recognize potential side effects.
Common Side Effects
The majority of people taking NAC do not experience severe side effects, but some common side effects include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Fatigue
It has been noted that these side effects are generally mild and decrease with time.
Considerations for Long-term Use
Long-term use of NAC might lead to:
- Oxidative stress at particularly high doses, conflicting with the antioxidant purpose of the supplement.
- Possible respiratory effects, with some studies indicating an increase in bronchospasm in people with asthma.
Long-term users should monitor these considerations closely and consult a healthcare provider regularly.
Interactions with Medications and Other Supplements
NAC may interact with certain medications and supplements. Key interactions include:
- Potential for increased bleeding risk when taken with blood-thinning medications like warfarin.
- Possible interference with antihypertensive drugs and nitroglycerin due to its vasodilatory effects.
- Alteration of immune system-related supplements and medications, as NAC may also have immuno-modulating effects.
A table summarizing the potential drug interactions:
| Drug/Supplement Type | Potential Interaction |
|---|---|
| Blood thinners | Increased bleeding risk |
| Antihypertensives | Altered blood pressure |
| Immune-modulating agents | Changed immune response |
Usage and Dosage Guidelines

N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) is a dietary supplement commonly used by bodybuilders to support various aspects of their training and health. It’s important for users to understand the proper intake, dosing variations, and timing for effective supplementation.
Recommended Intake for Bodybuilders
Bodybuilders typically take 600 to 1800 mg of NAC per day, divided into multiple doses. This supplement can come in various forms, including capsules, powders, and tablets. It’s important to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines or the advice of a healthcare professional when determining the exact dosage. Most bodybuilders start at the lower end of the spectrum and increase if necessary, based on their individual response and goals.
Adjusting Dosage Based on Individual Needs
NAC supplementation should be tailored to the individual. Factors such as body weight, overall health, and specific training goals can influence the optimal dose for each person. It’s advisable to begin with a lower dose to assess tolerance before gradually increasing. If one is taking other supplements or medications, it’s critical to consider potential interactions and consult with a healthcare provider.
Timing and Frequency of Supplementation
For bodybuilders, timing can be as important as the dose. NAC is often taken in 2-3 doses throughout the day, with one dose typically taken around training sessions to maximize its benefits. Consistent daily supplementation is recommended to maintain steady levels in the body. It should not be taken on an empty stomach, as it may cause gastrointestinal discomfort.
Exploring NAC Beyond Bodybuilding
N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) plays a role that extends beyond muscle recovery and performance enhancement. Its potential therapeutic applications in various health conditions are gaining interest in the medical community.
Potential in Treating Chronic Conditions
NAC has been studied as an adjunct therapy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and chronic bronchitis, where it helps to reduce mucus production and alleviate symptoms. Its antioxidant properties can also protect against liver damage and heart disease by countering the damage caused by oxidative stress. Homocysteine, an amino acid linked to heart disease, may be reduced as NAC modulates levels of glutathione, another antioxidant.
- COPD Management: Reduction of exacerbation frequency
- Heart Disease: Possible reduction in oxidative stress markers
Effect on Fertility and Reproductive Health
Research indicates that NAC could help improve fertility in both men and women. In men, it may enhance sperm quality and treat conditions such as varicocele, a common cause of infertility. Women could see improvements in fertility and pregnancy outcomes, more so among those with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
- Male Fertility: Improved seminal parameters
- Female Reproductive Health: Better ovulation rates in PCOS
Contributions to Cognitive and Neurological Functions
NAC acts as a precursor to the neurotransmitter glutamate, and in doing so, can have an impact on neurological functions. This suggests benefits for conditions like depression, Alzheimer’s disease, and possibly cancer, by promoting detoxification and balancing neurotransmitter levels.
- Cognitive Health: Improved symptoms in Alzheimer’s and depressive disorders
- Neuroprotective Effects: Potential inhibition of cancer cell proliferation
Frequently Asked Questions

Navigating the use of NAC in bodybuilding requires understanding its effects on muscle growth, performance, and overall health. This section offers insights into common queries about NAC supplementation for bodybuilders.
What is the recommended dosage of NAC for bodybuilders?
The recommended dosage of NAC (N-acetylcysteine) for bodybuilders typically falls between 600 to 1800 mg per day, divided into several doses. However, dosages should be personalized according to individual needs and a healthcare provider’s advice.
Can NAC impede muscle gains or athletic performance?
There is currently no substantial evidence to suggest that NAC supplementation impedes muscle gains or athletic performance. Some studies have indicated that NAC may help reduce fatigue and improve endurance.
How does NAC contribute to muscle growth and recovery?
NAC may contribute to muscle growth and recovery by supporting antioxidant defenses and reducing oxidative stress. This can help mitigate muscle damage and inflammation, potentially leading to improved recovery times.
When is the optimal time to take NAC in relation to a workout?
The optimal time to take NAC is often recommended to be 30 minutes to an hour before a workout, providing the body with sufficient time to absorb the antioxidant and potentially improve performance and minimize muscle damage.
How does NAC affect testosterone levels in bodybuilders?
There is limited research on NAC’s direct effects on testosterone levels in bodybuilders. Bodybuilders should consult with a healthcare professional regarding NAC’s potential hormonal impacts and any related concerns.
What are the potential side effects of taking NAC as a supplement?
Potential side effects of taking NAC can include gastrointestinal discomfort, nausea, vomiting, and headache. Chronic high doses may lead to more serious side effects, and it is essential to follow recommended guidelines and consult with a healthcare provider.
References
- International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism Study on NAC and Fatigue: https://journals.humankinetics.com/view/journals/ijsnem/14/3/article-p298.xml
- The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism on Antioxidants and Testosterone: https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article/96/7/E1105/2834258
- [1] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC436956/
- [3] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26763748/
- [5] https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40263-019-00680-w
- [6] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5241507/
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 12035, Acetylcysteine. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/N-Acetylcysteine.
- The role of N-acetylcysteine in the management of oxidative stress and inflammation in skeletal muscle: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4526841/
Author

Dr. Aditya K. Sharma
I am Dr. Aditya Sharma, a dedicated urologist specializing in kidney transplants and advanced urological surgeries. My career is driven by a passion for delivering exceptional care and pioneering surgical techniques. Outside the operating room, I have a keen interest in studying the effects of anabolic steroids on bodybuilding, seeking to understand the fine line between enhancing performance and maintaining health.